Data Structures: Trees Explained for Beginners
Trees are one of the most important data structures in computer science. They are widely used in databases, file systems, search engines, and artificial intelligence. Understanding trees helps you design efficient algorithms and solve complex problems.
In this article, you will learn what trees are, how they work, and why they are so important in programming.
What Is a Tree in Data Structures?
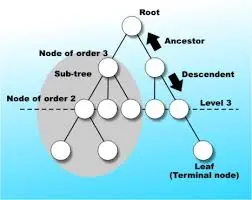
A tree is a hierarchical data structure made up of nodes. Each node contains a value and links to other nodes. Unlike arrays or lists, a tree represents data in a parent-child relationship.
A tree starts with a root node, and every other node is connected to it directly or indirectly.
Basic Terminology of Trees
To understand trees clearly, you need to know some basic terms.
Root
The topmost node in a tree.
Parent
A node that has one or more child nodes.
Child
A node that descends from another node.
Leaf
A node that has no children.
Edge
The connection between two nodes.
Example of a Tree Structure
A
/
B C
/
D E F
A is the root
B and C are children of A
D and E are children of B
F is a child of C
Types of Trees
There are many types of trees used in programming.
Binary Tree
A tree where each node can have at most two children.
Binary Search Tree (BST)
A special type of binary tree where:
Left child contains smaller values
Right child contains larger values
Balanced Tree
A tree where the height difference between left and right subtrees is minimal.
Binary Heap
Used in priority queues and heap sort algorithms.
Why Trees Are Important
Trees help in:
Fast searching and sorting
Organizing hierarchical data
Representing file systems
Database indexing
Artificial intelligence and machine learning
Without trees, many modern applications would be inefficient.
Tree Traversal Methods
Traversal means visiting all nodes in a specific order.
Inorder Traversal
Left → Root → Right
Preorder Traversal
Root → Left → Right
Postorder Traversal
Left → Right → Root
Each traversal method is used for different tasks such as expression evaluation and tree reconstruction.
Example of Tree Node in Python
class Node:
def __init__(self, value):
self.value = value
self.left = None
self.right = None
This creates a basic structure for a binary tree node.
Inserting Data in a Binary Tree
def insert(root, value):
if root is None:
return Node(value)
if value < root.value:
root.left = insert(root.left, value)
else:
root.right = insert(root.right, value)
return root
This example shows how values are added based on comparison.
Real-World Applications of Trees
File systems in operating systems
Database indexing (B-Trees)
Compiler syntax trees
Artificial intelligence decision trees
Search engines
Trees help manage and process large data efficiently.
Common Mistakes Beginners Make
Confusing tree with graph
Forgetting base cases in recursion
Incorrect traversal logic
Not balancing the tree
Avoiding these mistakes improves understanding and code quality.
Why You Should Learn Trees
Learning tree data structures improves your problem-solving skills and helps you understand advanced concepts like graphs and algorithms.
Trees are heavily used in competitive programming, interviews, and real-world applications.
Conclusion
Trees are powerful data structures that represent hierarchical data efficiently. From file systems to artificial intelligence, trees play a vital role in modern computing.
By mastering tree concepts, you build a strong foundation for advanced programming topics and real-world problem-solving.